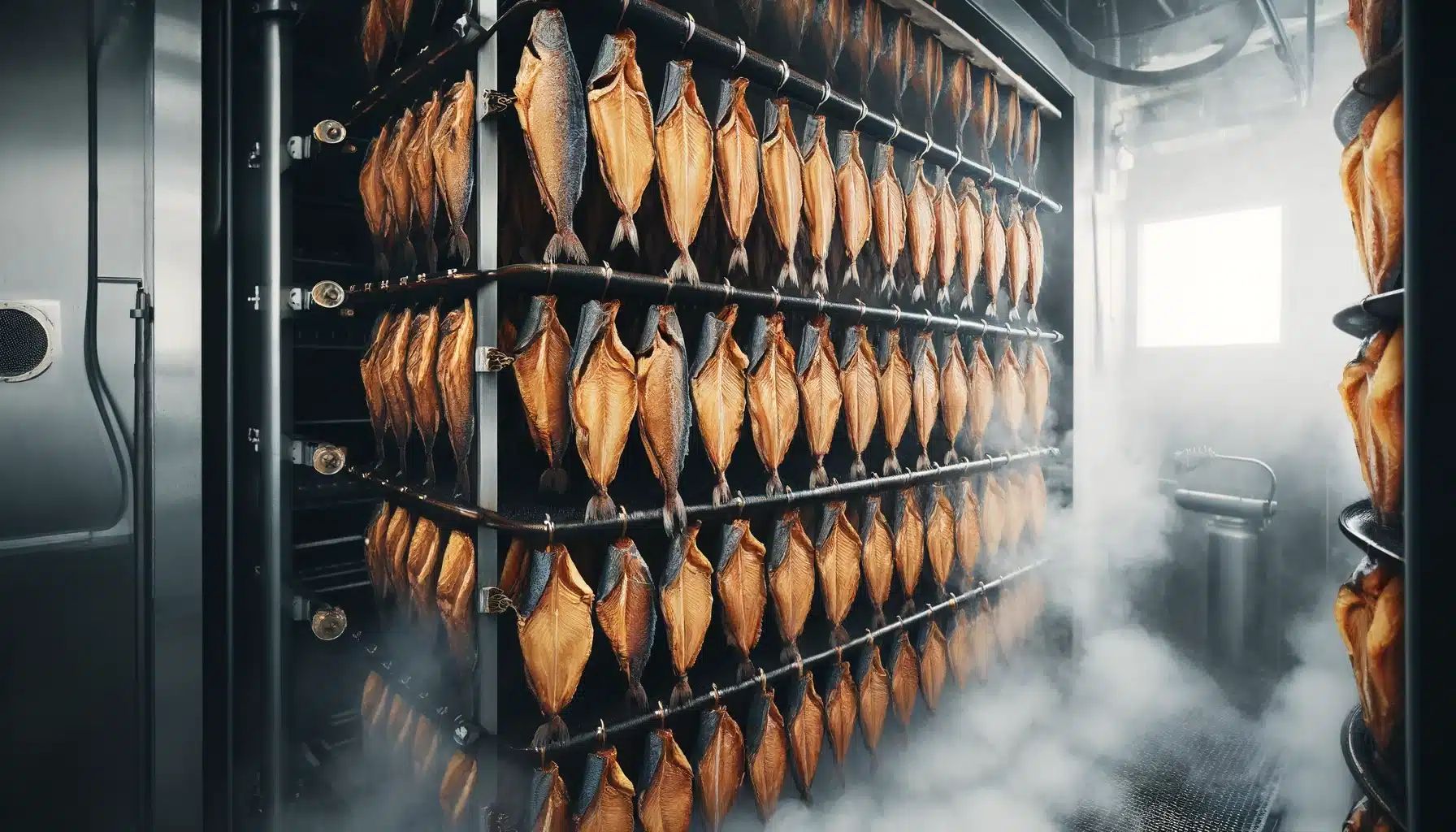
Cold smoking is a traditional method of preserving fish that has been practiced for centuries. It involves smoking fish at low temperatures, typically between 68-86°F (20-30°C), for an extended period of time, usually several days. This process imparts a rich, smoky flavor to the fish while also preserving it by reducing moisture content and inhibiting the growth of bacteria and other microorganisms. Cold smoking is a popular method for preserving fish such as salmon, trout, mackerel, and herring, and is widely used in the food industry to produce a variety of cold smoked fish products.
Cold smoking is a delicate process that requires careful control of temperature, humidity, and smoke concentration to ensure the safety and quality of the final product. The traditional method of cold smoking involves hanging the fish in a smokehouse and allowing the smoke from smoldering wood chips to slowly permeate the flesh. However, in industrial settings, modern equipment and machinery are used to automate and control the cold smoking process, allowing for greater consistency and efficiency in production.
Industrial Cold Smoking Process
In industrial cold smoking, the process begins with the selection of high-quality fish that is then cleaned, gutted, and filleted before being brined or dry-cured to enhance flavor and texture. The fish is then transferred to a smokehouse where it is exposed to controlled levels of smoke and heat for a specified period of time. The smoke is generated by burning wood chips or sawdust in a separate chamber, and the resulting smoke is channeled into the smokehouse where it circulates around the fish, imparting its characteristic flavor and aroma.
Industrial cold smoking processes typically use a combination of mechanical and electronic systems to regulate temperature, humidity, and smoke concentration. This ensures that the fish is smoked at the correct temperature for the appropriate duration, resulting in a consistent and high-quality product. The use of modern technology also allows for greater control over the smoking process, reducing the risk of spoilage or contamination and ensuring that the final product meets strict quality and safety standards.
Quality Control and Safety Measures
Quality control and safety measures are of paramount importance in industrial cold smoking to ensure that the final product is safe for consumption and meets regulatory requirements. This includes rigorous testing of raw materials, monitoring of processing conditions, and regular inspections of equipment and facilities. Quality control measures also encompass sensory evaluation of the finished product to assess its appearance, texture, flavor, and aroma.
In addition to quality control, safety measures are implemented to minimize the risk of foodborne illness and ensure that the cold smoked fish is free from harmful pathogens and contaminants. This includes strict adherence to hygiene and sanitation practices, as well as the implementation of Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) protocols to identify and mitigate potential hazards throughout the production process. Regular microbiological testing is also conducted to verify the absence of harmful bacteria such as Listeria monocytogenes and Clostridium botulinum.
Equipment and Machinery Used in Industrial Cold Smoking
Industrial cold smoking relies on a range of specialized equipment and machinery to automate and control the smoking process. This includes smokehouses, smoke generators, temperature and humidity controls, and ventilation systems. Smokehouses are designed to accommodate large volumes of fish and are equipped with racks or trolleys to hold the fish during smoking. Smoke generators produce smoke by burning wood chips or sawdust, which is then channeled into the smokehouse through a network of ducts or pipes.
Temperature and humidity controls are essential for maintaining the ideal conditions for cold smoking, ensuring that the fish is smoked at the correct temperature and humidity levels for the required duration. Modern smokehouses are equipped with electronic controllers that allow for precise regulation of these parameters, reducing the risk of over- or under-smoking. Ventilation systems are also important for maintaining air circulation within the smokehouse, preventing the buildup of stale smoke and ensuring even distribution of smoke around the fish.
Packaging and Storage of Cold Smoked Fish
Once the cold smoking process is complete, the fish is carefully removed from the smokehouse and prepared for packaging. Cold smoked fish is typically vacuum-sealed or packed in modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) to extend its shelf life and preserve its quality. Vacuum-sealing removes air from the packaging, preventing oxidation and reducing the risk of spoilage, while MAP involves replacing air with a mixture of gases such as carbon dioxide and nitrogen to inhibit microbial growth.
Proper storage is essential for maintaining the quality and safety of cold smoked fish. It should be stored at refrigerated temperatures (32-39°F or 0-4°C) to prevent bacterial growth and maintain its freshness. The packaging should also be labeled with information such as production date, expiration date, storage instructions, and nutritional information to inform consumers about the product and ensure its safe consumption.
Regulatory Compliance and Certification
Industrial cold smoking operations are subject to stringent regulatory requirements to ensure food safety and quality. This includes compliance with national and international standards such as Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA), and European Union regulations on food hygiene and safety. In addition to regulatory compliance, many cold smoking facilities also seek certification from third-party organizations such as the Safe Quality Food (SQF) Institute or British Retail Consortium (BRC) to demonstrate their commitment to producing safe and high-quality products.
Certification involves rigorous audits of production facilities, processes, and documentation to verify compliance with industry standards. This includes assessments of hygiene practices, sanitation procedures, pest control measures, traceability systems, and employee training programs. Certification provides assurance to consumers and retailers that cold smoked fish products have been produced in accordance with strict quality and safety standards, enhancing their marketability and consumer confidence.
Advantages and Challenges of Industrial Cold Smoking
Industrial cold smoking offers several advantages over traditional methods, including greater efficiency, consistency, and scalability in production. Modern equipment and technology allow for precise control over smoking conditions, resulting in a more uniform product with consistent flavor and quality. Industrial cold smoking also enables higher volumes of fish to be processed, meeting the demands of commercial markets while maintaining product integrity.
However, industrial cold smoking also presents challenges related to cost, complexity, and regulatory compliance. The initial investment in equipment and facilities can be substantial, requiring careful planning and financial resources. The complexity of modern smoking systems also necessitates skilled personnel with expertise in operating and maintaining the equipment. Regulatory compliance adds another layer of complexity, requiring ongoing monitoring, documentation, and verification to ensure adherence to food safety standards.
In conclusion, industrial cold smoking plays a vital role in meeting consumer demand for high-quality cold smoked fish products while ensuring food safety and regulatory compliance. The use of modern equipment and technology allows for greater control over the smoking process, resulting in consistent products that meet strict quality standards. However, this comes with challenges related to cost, complexity, and regulatory compliance that must be carefully managed to ensure successful operation in this specialized sector of the food industry.